Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity?
What Cybersecurity Means to Me
- Cybersecurity is about building trust. In the security field, there is a saying: “There is no free lunch for security.” This means that enhancing security inevitably involves costs. However, true security professionals know how to balance this cost with security needs. They understand the required security level for each type of data, focusing on risk management rather than striving for zero risk.
- Many people think that enhancing security makes systems harder to use or decreases performance. Security professionals must find ways to strengthen security while minimizing these inconveniences and should strive to enhance security without impacting performance. Additionally, when inconvenience is necessary, they must be able to persuasively explain with data why it is essential. Therefore, security is an area that requires teamwork, effective communication, and the technical skill to reach a good consensus among stakeholders.
Cyber Security Principles to Consider
- Principle of Data/Code Isolation: Data should be clearly separated from code to prevent unintended data access or modification, thereby enhancing security.
- Principle of Least Privilege: All programs and privileged users should operate with only the minimum privileges necessary to complete their tasks, thereby reducing unauthorized access and security incidents.
- Defense in Depth: This strategy involves deploying multiple layers of security to reduce risks from a single point of failure. Even if attackers access the system, the additional layers enhance protection.
- Fail-Safe Defaults: Systems should maintain secure default settings. Unless specifically granted permissions, the default should be restricted access.
- Complete Mediation: This principle requires that all access is centrally controlled and logged, ensuring every access request is checked and only authorized users can gain access.
- Economy of Mechanism: Security systems should be as simple and easy to maintain as possible. Simple systems are less prone to errors and vulnerabilities, making them more secure.
- Open Design: Security systems should not rely on secrecy of the design. A secure system should maintain its security even when its design is open to public scrutiny.
My Skills and Strengths
- I possess a comprehensive understanding of security, with advanced knowledge particularly in penetration testing for web and mobile applications.
- I possess leadership skills that enable me to effectively communicate with people and achieve shared goals. Drawing from my experience as a team leader, I have consistently developed my interpersonal skills and have a particular strength in building extensive networks. I approach collaborative challenges with a positive and constructive mindset, finding opportunities for growth in situations that others might find stressful, rather than being overwhelmed by them.
- I have project and resource management abilities. I prepare WBS annually and consistently receive recognition from managers for being the most organized team member.
- I am committed to continuous learning and curiosity. Recently, I completed an 8-month program in AI, and I am frequently recognized for my broad interest in various fields beyond computer science.
My Career Path
- Ultimately, I want to work in management. My goal is to become a Tech Leader with strong technical skills and understanding. I envision myself as a startup CEO, corporate executive, or departmental leader. I prefer a role where I guide my team toward shared objectives and provide direction, rather than serving as an individual contributor.
- Therefore, I aim to be a generalist with a broad understanding across fields, rather than deep expertise in a single area. My focus is on cybersecurity, while also gaining knowledge in software engineering and AI. I want to leverage teamwork and collaboration to fill any gaps rather than doing it all alone.
- My next roles could include positions like Application Security Engineer, Security Engineer, or Security Architect.
- Back in 2021, I believed that a Software Engineer background offered more job options. However, with recent advances in AI, I think it’s more advantageous to continue focusing on cybersecurity while developing code quality skills. My goal is not merely to be a skilled hacker but to advance my career as a security leader.
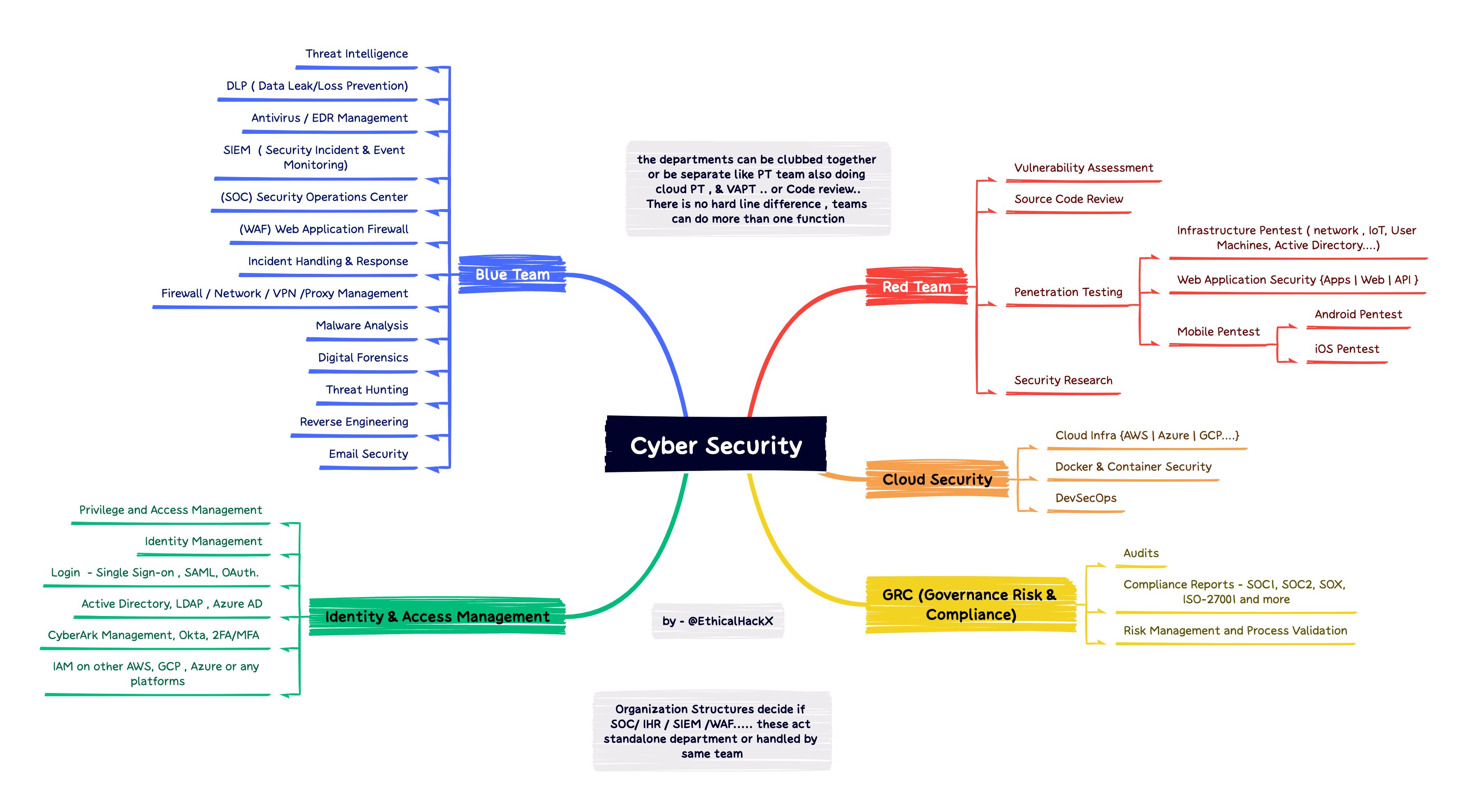
Cybersecurity Career Tracks
- Analysts: Focus on identifying, monitoring, and addressing vulnerabilities. Their primary role is to detect and analyze security risks.
- Security Engineers: Responsible for building defensive systems based on security architecture designs. This role can specialize into areas like:
- Network Security Engineers
- Cloud Security Engineers
- Security Operations Engineers
- Incident Response: The first team to respond to security incidents. They play a crucial role in detecting and resolving security events, often requiring collaboration with multiple departments.
- Digital Forensics: Analyzes cyberattacks and prepares legal evidence to support investigations and prosecutions.
- GRC Roles: Primarily focus on managing legal and regulatory compliance, providing training, and handling risk management. They are also responsible for educating other departments and are often performed by security leaders.
- Security Architecture: Requires extensive experience across various domains and at least three years of security experience. Responsible for designing solutions or products with a strong security mindset.
- IAM Analyst: Manages and designs IAM (Identity and Access Management) processes and resources.
- IAM Engineer: Designs, builds, and maintains IAM tools and systems.
What I Need to Do
- Solve Hack The Box challenges and gain experience in CTF competitions.
- Strengthen my understanding of algorithms by solving LeetCode problems.
- Obtain certifications.
- Contribute to open source projects.
- Study Google’s materials on code quality and document my learning on my blog.
- Participate in bug bounties to earn rewards.
- File patents and contribute PoCs for CVEs.
- Set a goal to pursue an MBA at Stanford and explore a 529 plan if relocation becomes necessary.
나에게 있어 보안이란?
- 보안은 신뢰감을 형성하는 것이다. 보안 업계에는 “There is no free lunch for security”라는 말이 있다. 즉, 보안을 강화하려면 반드시 비용이 따른다는 의미다. 하지만 진정한 보안 전문가는 이 비용과 보안의 밸런스를 조절할 줄 아는 사람들이다. 그들은 보안과 편리함 사이에서 균형을 맞추는 방법을 알고 있으며, 각 데이터가 요구하는 보안 수준을 명확히 이해하고 리스크 제로보다는 리스크 관리에 초점을 맞출 수 있어야 한다.
- 많은 사람들은 보안을 강화하면 사용이 불편해지거나 성능이 저하된다고 생각한다. 보안 전문가는 이러한 불편을 최소화하면서도 보안을 강화할 수 있는 방법을 찾아내야 하며, 성능에 영향을 주지 않고 보안을 높일 수 있는 방안을 연구해야 한다. 또한, 불편을 감수할 필요가 있는 경우라면, 왜 그러한 불편이 필요한지, 그리고 그것이 얼마나 중요한지를 데이터를 기반으로 설득할 수 있어야 한다. 따라서 보안은 철저한 팀워크이자 이해관계자들 사이에서 좋은 합의점을 도출할 수 있는 대화 및 기술이 필요한 영역이다.
내가 생각해야 할 보안의 원칙
- 데이터/코드 격리 원칙: 데이터는 코드와 명확히 분리되어야 한다. 이를 통해 의도치 않은 데이터 접근이나 변경을 방지하고 보안성을 높일 수 있다.
- 최소 권한 원칙: 모든 프로그램과 시스템의 권한을 가진 사용자들은 필요한 최소한의 권한만으로 작업을 수행해야 한다. 이렇게 함으로써 불필요한 접근을 제한하고, 권한 남용이나 보안 사고를 줄일 수 있다.
- 방어 심층화 원칙 (Defense in Depth): 여러 보안 방어층을 겹겹이 배치하여 단일 실패 지점에 의한 위험을 줄이는 전략이다. 공격자가 시스템에 접근하더라도, 추가 방어층을 통해 시스템 보호를 강화할 수 있다.
- 기본 방어 원칙 (Fail-Safe Defaults): 시스템이 기본적으로 안전한 설정을 유지해야 한다는 원칙이다. 사용자나 시스템이 특별히 권한을 부여하지 않는 한 기본 설정으로 접근이 제한되도록 해야 한다.
- 완전 중재 원칙 (Complete Mediation): 시스템에서 모든 접근이 중앙에서 통제되고 기록되는 원칙이다. 이는 모든 접근 요청이 반드시 검토되고, 허가된 사용자만 접근할 수 있도록 보장한다.
- 보안의 경제성 원칙 (Economy of Mechanism): 보안 시스템은 가능하면 단순하고, 이해하기 쉬우며 유지보수가 용이해야 한다. 간단한 시스템이 오류와 취약점이 발생할 가능성이 낮아 보안적으로 안전하다.
- 공개 설계 원칙 (Open Design): 보안 시스템은 비밀스러운 설계에 의존하지 않아야 한다. 안전한 시스템은 설계가 공개된 상태에서도 보안성을 유지할 수 있어야 한다.
내가 가지고 있는 역량
- 보안 전반에 걸쳐 기본적인 이해를 가지고 있으며, 특히 웹과 모바일의 침투 테스트(penetration testing) 분야에서 심화된 지식을 갖추고 있다.
- 사람들과 소통하며 목표를 효과적으로 달성할 수 있는 리더십 능력을 갖추고 있다. 많은 팀 리더로서의 경험을 바탕으로 대인관계 기술을 꾸준히 발전시켜 왔으며, 폭넓은 네트워크 형성에 강점을 가지고 있다. 사람들과의 협업 과정에서 발생하는 도전적인 상황들을 긍정적이고 건설적인 방식으로 접근하며, 이러한 과정에서 스트레스보다는 성장의 기회를 발견한다.
- 프로젝트 및 리소스에 대한 관리 능력을 가지고 있다. 매년 WBS를 작성하고, 팀에서 가장 체계적으로 일하는 사람으로 매니저에게 평가받았다.
- 끊임없는 호기심과 배움의 자세를 가지고 있다. 최근에는 AI 영역의 8개월 프로그램을 수료하였으며, 단순한 컴퓨터 과학뿐만 아니라 다양한 분야에 대한 관심이 많다는 평가를 받고 있다.
- 보안인력이 1000명 이상 되는 기업은 사실상 많이 없다. 그런 기업에서 일을 하며 보안이 잘 갖추어진 조직에서의 보안 경험은 큰 자산중에 하나이다. 전체 인력의 4%에 육박하는 보안 투자 기업에서 일했었다. 보통의 기업은 보안 인력이 전체 인력의 0.1% ~ 0.5%에 그친다.
내가 추구하는 커리어 path
- 최종적으로 매니지먼트 쪽에서 일하고 싶다. 충분한 기술 역량과 이해를 갖춘 Tech 리더가 되는 것을 목표로 한다. 스타트업의 CEO가 될 수도, 기업의 임원이 될 수도, 혹은 부서 리더가 될 수도 있다. 단순한 IC보다는 팀원들과 함께 목표를 공유하고 방향성을 제시하는 리더로서 활동하고 싶다.
- 따라서 한 분야의 깊은 전문성보다는 여러 분야에 걸친 폭넓은 이해를 가진 제너럴리스트가 되고 싶다. 이 과정에서 사이버 보안을 중심으로 소프트웨어 엔지니어링, AI 등의 지식을 갖추고, 부족한 부분은 팀워크와 협업을 통해 보완하고자 한다.
- 다음 직군으로 Application Security Engineer, Security Engineer, Security Architect 등의 포지션을 고려하고 있다.
- 2021년에만 해도 Software Engineer 경력이 더 유리하다고 생각했으나, 최근 AI의 발전을 보며 코드 품질에 대한 역량을 잘 갖춘다면 사이버 보안에 중점을 두고 커리어를 이어나가는 것이 더 유리할 것이라 생각한다. 단순히 해킹을 잘 하는 해커가 되는 것을 추구하는 것이 아니라 보안 전문 리더로서 커리어를 발전시키고자 한다.
- 하지만 위에 말한 커리어는 적어도 OSCP와 같은 자격증을 보유하고 내가 해킹에 대해 선두에 설순 없지만 어느정도 할 수 있다는 역량이 길러지기 전까지는 가지 않겠다. 그 전까지는 Offensive security engineer로 가길 희망한다.
해커란?
- 문득 철학자와 같다는 생각을 하게 되었다. 해커에게 있어서 중요한 역량중에는 호기심이 많고 당연한 것을 당연하게 받아들이지 않고 끊임 없이 의심하면서 그 지점을 찾아나가는 사람들인것이다. 그와 동시에 과거에 있었던 기법들을 단순히 기법자체를 알기보다 왜 그렇게 되었고 지금은 왜 이렇게 발전하게 되었는지에 대해 아는 것으로 자신만의 또 다른 앞을 개척해나가기 때문에 철학과 많이 닮아있다고 생각한다.
Cybersecurity Career Tracks
- Analysts: 취약점들에 대해 찾고 모니터하고 관련 일을 하는 쪽이다.
- Security Engineers: Security architects design과 관련된 방어적인 부분들을 building하는 역할이다. Network Security Engineers, Cloud Security Engineers, Security Operation Engineers등으로 세분화 될 수도 있다.
- Incident Response: 보안 사건이 터졌을 때 가장 먼저 반응 하는 팀이고 그 문제들을 detect하는 역할을 한다. 많은 부서와의 협약이 필요하다.
- Digital forensics: 사이버 공격에 관해 분석하고 법적인 증거를 제출 할 수 있도록 준비하는 역할들을 한다.
- GRC roles: 전반적인 법률 규제와 관련된 관리하고 교육시키며 위험 부담에 대한 매니징을 주로한다. 다른 부서의 교육 또한 책임진다. 보안 리더들이 주로 하는 일이다.
- Security Architecture: 여러 도메인에 경험이 있는 것이 도움이 되고 보안에 3년 이상의 경력으로 security mindset을 지닌 상태로 솔루션 혹은 프로덕트의 전반적인 디자인을 책임진다.
- IAM Analyst: IAM 프로세스나 리소스를 관리하고 디자인하는 역할을 한다.
- IAM Engineer: IAM 관련 도구들을 design, build, maintains하는 역할을 한다.
내가 해야 하는 일
- Hack The Box 문제를 해결하고, CTF 대회에서 입상 경험 쌓기.
- LeetCode 문제를 통해 알고리즘 역량을 강화하기.
- 자격증 취득. (CISSP, OSCP, CCSE 공부하기)
- 오픈 소스 프로젝트에 기여하기.
- Google의 코드 품질 관련 자료를 읽고, 블로그에 정리하여 학습 결과를 공유하기.
- 버그 바운티에 참여하여 상금 획득.
- 각종 특허 발표 및 CVE에 PoC 기여.
- Stanford MBA 진학 목표 설정 및 필요 시 529 플랜 준비.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.